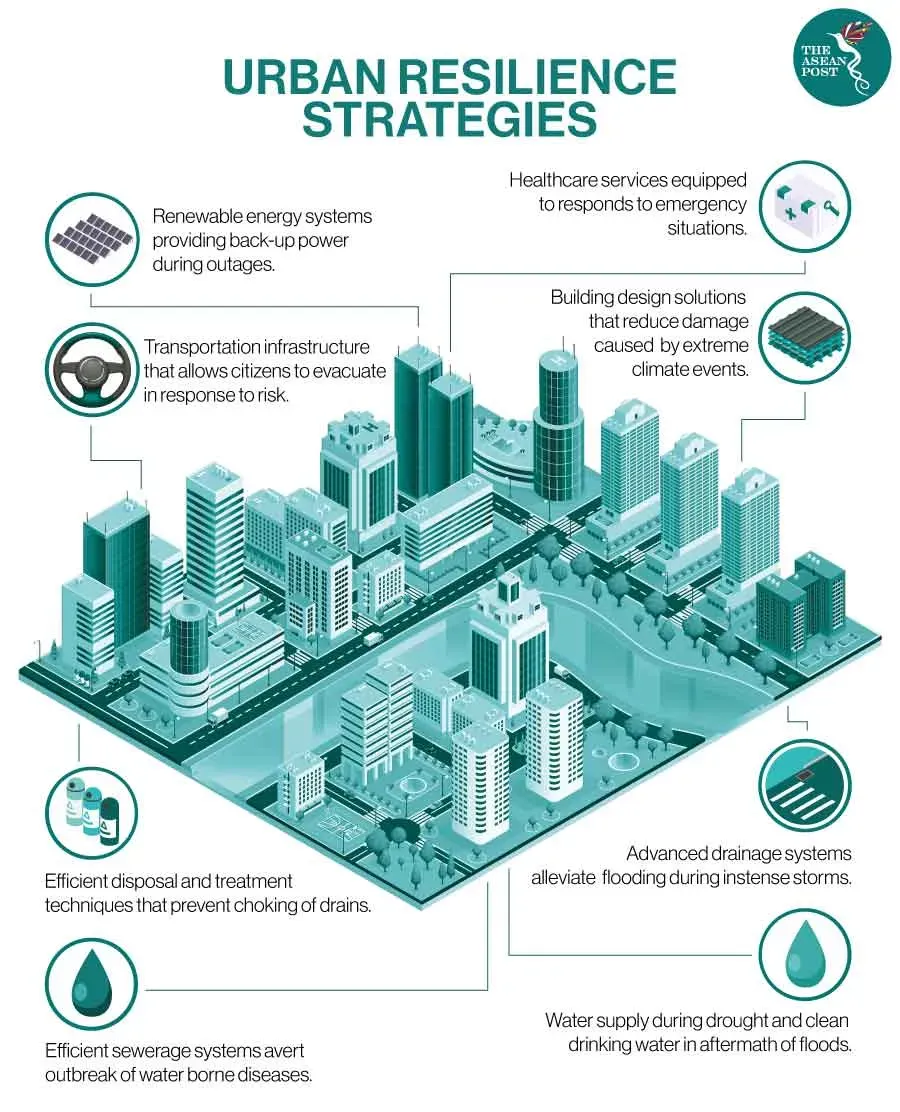
Urban climate resilience is the foundation for safer, healthier cities as they confront rising temperatures, intensifying storms, creeping flood risks, and the everyday pressures of a changing weather regime. As the planet warms, heat waves and heavy rainfall become everyday realities, disrupting critical infrastructure, straining budgets, and affecting the health and livelihoods of residents across neighborhoods. Building resilience means more than reacting to disasters; it requires proactive planning, inclusive governance, data-informed decision making, and a shared commitment to safer neighborhoods and equitable outcomes. This approach aligns with city resilience strategies that blend science, finance, community engagement, and thoughtful design to safeguard housing, transport, water, energy, and public health in the face of climate hazards. By focusing on planning that remains flexible over time and supported by case-based investments, communities can reduce vulnerabilities and lay the groundwork for sustainable growth for all residents.
Viewed through an alternative frame, the challenge becomes urban resilience to climate shocks, where planners map risk, test scenarios, and invest flexibly. This framing emphasizes the systems that absorb heat, flood, and disruption, keep essential services running, and support continuous social and economic life. LSI-informed phrasing weaves in adaptive planning for urban areas, climate risk management, nature-based solutions, and equitable outcomes. Public engagement, data-driven decision making, and scalable investments help cities stay ahead of changing conditions and deliver benefits for all residents.
Urban Climate Resilience: Integrating Resilient Infrastructure and Adaptive Planning
Urban climate resilience centers on cities anticipating and preparing for climate-related shocks, then responding and recovering with speed and equity. As cities adapt to climate change, integrating resilient infrastructure with adaptive planning for urban areas allows municipalities to reduce exposure to heat waves, floods, and storms while protecting vulnerable residents. This approach embodies city resilience strategies that blend science, policy, and inclusive governance to bend the curve toward safer, healthier, and more equitable urban life.
Implementing urban climate resilience requires a toolkit that combines risk diagnostics, modular infrastructure, and nature-based solutions. Real-time dashboards and open risk maps help citizens understand exposure and participate in resilience planning, while investments in climate-resilient buildings, flood defenses, and reliable energy networks ensure critical services endure shocks. By prioritizing no-regret options that perform well across multiple futures, cities advance climate adaptation in cities and strengthen adaptive capacity for urban areas.
Governance, Equity, and Nature-Based Solutions: Advancing Climate Adaptation in Cities
Effective city governance lies at the heart of climate adaptation in cities. Transparent planning, cross-sector collaboration, and inclusive engagement ensure that city resilience strategies reach all residents, including renters and vulnerable populations. Nature-based solutions—trees, green roofs, parks, wetlands, and permeable surfaces—deliver cooling, flood protection, and improved air quality while delivering social and economic co-benefits that support urban climate resilience.
From measuring success to scaling, governance must align with budgets and finance mechanisms that support resilient infrastructure and equitable outcomes. Collaborative partnerships among municipal agencies, private developers, researchers, and communities accelerate climate adaptation in cities, ensuring that city resilience strategies address housing, transportation, water, and energy. By focusing on indicators such as exposure reduction, service continuity, and inclusive public engagement, cities can drive continuous improvement and learning in urban resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is urban climate resilience and why is it essential for cities adapting to climate change?
Urban climate resilience is a city’s ability to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from climate shocks and stresses. It blends governance, data-driven risk assessment, resilient infrastructure, nature-based solutions, and inclusive planning to protect people and economies as heat waves, floods, storms, and sea-level rise intensify. By planning for multiple futures rather than a single forecast, cities can reduce exposure, ensure quicker recovery, and deliver safer, healthier, and more equitable urban life through proactive investment and collaborative decision‑making.
What practical steps underpin city resilience strategies for climate adaptation in cities, and how does adaptive planning for urban areas help?
Core steps include cool and green infrastructure to reduce heat islands; water-sensitive urban design to manage storms; climate-smart mobility to keep services moving; stronger building standards and retrofits; expanding energy resilience with microgrids and backup power; and robust early warning systems. Adaptive planning adds rolling risk assessments, modular infrastructure, and performance-based standards, plus broad public engagement so plans reflect local needs and can scale as conditions change. Together, these actions build city resilience strategies that are actionable, scalable, and equitable across neighborhoods.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition | Urban climate resilience is the city’s ability to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from climate-related shocks and stresses, with an emphasis on proactive planning, inclusive governance, and smart investments that protect people and infrastructure. |
| Understanding | Cities are complex systems where science, policy, and community action must work together to reduce risk and enable quick, equitable recovery after climate events. |
| Core Pillars | Governance and planning; Data and risk diagnostics; Resilient infrastructure; Nature-based solutions; Social equity and inclusion. |
| Practical Strategies | Cool and green infrastructure; Water-sensitive urban design; Climate-smart mobility; Building standards and retrofits; Energy resilience; Early warning and response. |
| Infrastructure & Planning | Designing for tomorrow’s risks, scenario planning, no-regret investments, and integrating resilience into land-use planning to guide growth toward safer, more adaptable neighborhoods. |
| Adaptive Planning | Rolling risk assessments; Modular infrastructure; Performance-based standards; Public engagement to reflect local needs and values. |
| Case Studies | Rotterdam: water plazas and green corridors; Singapore: diversified water sources and integrated drainage; New York City: coastal protection and resilient infrastructure post-Sandy; Copenhagen: bike-friendly, green infrastructure. |
| Measuring Success | Exposure and vulnerability metrics; infrastructure performance during extremes; climate adaptation and energy resilience metrics; economic and social outcomes; public engagement. |
| Challenges & Opportunities | Funding gaps, governance fragmentation, and competing priorities; however, aligning resilience with housing, health, and economic goals unlocks co-benefits through collaboration. |
| Community Role | Local knowledge, inclusive planning, equitable engagement, and empowerment to drive behavior changes and strengthen social cohesion. |
| Vision & Conclusion | Adaptive planning, scalable solutions, and shared responsibility across sectors to build safer, livable cities that thrive in a warming world. |